Restore and Revitalize with Certified Manual Therapy
- Relieves muscle tension and joint stiffness
- Promotes natural healing through hands-on techniques
- Improves mobility and overall function
- Reduces pain from chronic or acute injuries
- Enhances posture and alignment
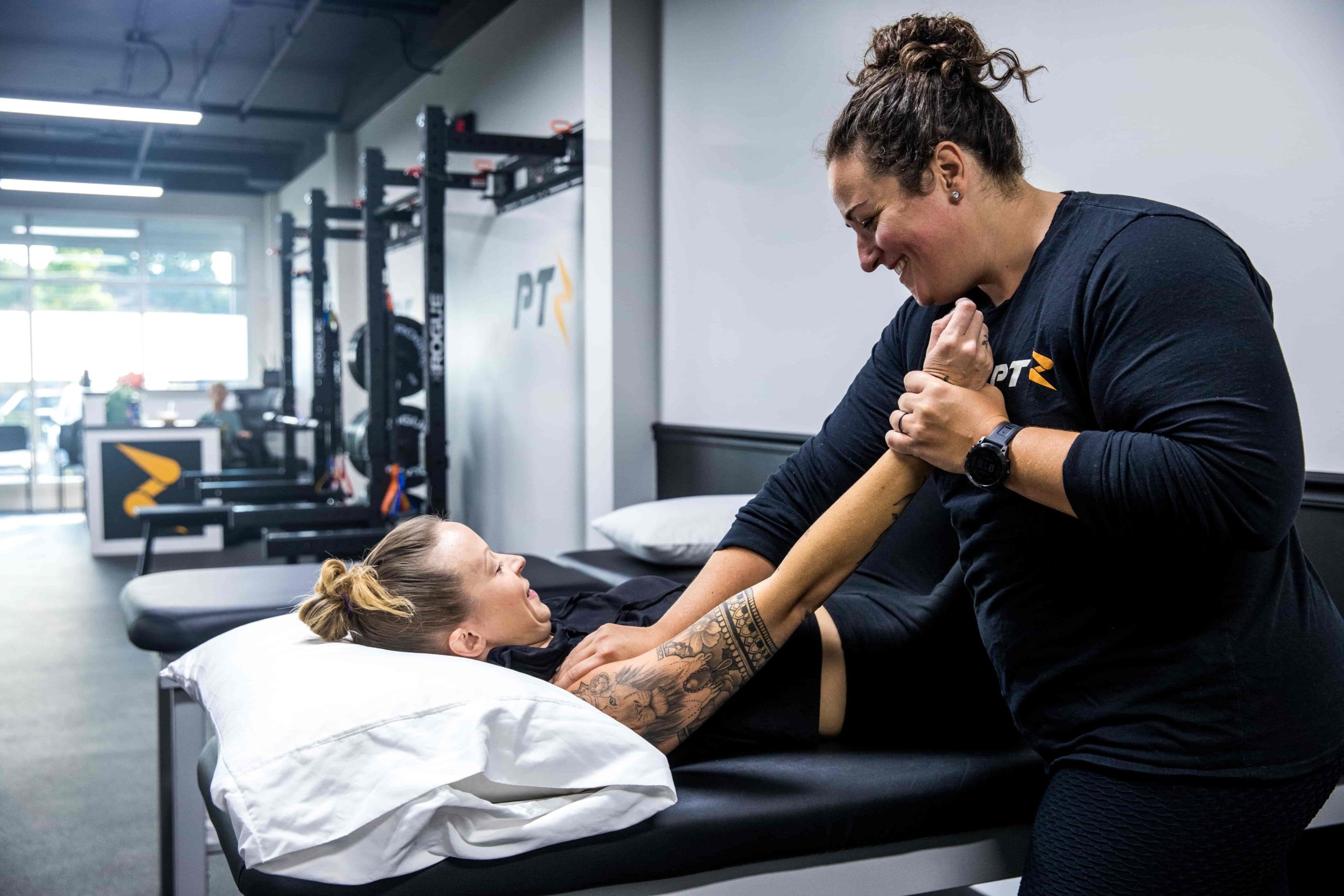

What is Certified Manual Therapy and
How Does It Help?
Certified Manual Therapy (CMT) is a specialized approach to musculoskeletal care where a trained therapist uses hands-on techniques to diagnose and treat soft tissues and joint structures. Unlike passive treatments that solely rely on machines, CMT focuses on the expert touch, providing targeted mobilizations, manipulations, and massage that address the root causes of pain and dysfunction. By blending science and a skilled practitioner’s intuition, Certified Manual Therapy offers a potent path toward better mobility, posture, and lasting relief.
These hands-on techniques help to ease muscle spasms, correct joint misalignments, and improve circulation, all of which accelerate the body’s natural healing processes. Manual therapy can be particularly effective in relieving chronic issues that stem from repetitive strain or past injuries, as well as providing essential support for acute trauma recovery. By stimulating blood flow and promoting tissue health, Certified Manual Therapy sets the stage for faster rehabilitation and decreased reliance on medications.
What truly distinguishes Certified Manual Therapy is the personalized approach: your therapist closely monitors how your tissues respond, adjusting techniques to meet your specific needs in real time. This level of care ensures each session is both comfortable and productive, allowing you to progress steadily toward your goals. When integrated with exercises and other therapeutic interventions, CMT can help you return to your favorite activities sooner—and stay healthier in the long run.
By addressing the underlying mechanics of your joints and soft tissues, Certified Manual Therapy not only reduces pain but also helps resolve the movement restrictions that often lead to re-injury. Techniques such as joint mobilization, myofascial release, and trigger point therapy help break down scar tissue, ease stubborn knots, and enhance joint fluidity. This translates to better range of motion, improved posture, and a renewed sense of stability in your daily life.
Combined with guidance on posture correction and active strengthening, CMT paves the way for holistic healing. It can help athletes overcome performance-limiting aches or support anyone seeking a noninvasive route to alleviate pain. As an integral part of a comprehensive physical therapy plan, Certified Manual Therapy is a powerful catalyst for getting you back to doing what you love—with greater ease and confidence.

In The Zone
Conditions Certified Manual Therapy Can
Help Address: (A-Z)
ACL Tear
Manual therapy addresses stiffness and scar tissue formation post-surgery or injury, promoting proper knee mechanics. By loosening tight soft tissues and improving joint mobility, it aids in speeding recovery and ensuring optimal function. This hands-on approach also helps reduce pain and fosters smoother movement for a safer return to activity.
Achilles Rupture
Certified Manual Therapy relieves tension in the calf and ankle structures, breaking down adhesions that slow healing. Carefully applied techniques improve flexibility in the Achilles region while reducing pain. As a complement to exercise, this hands-on care fosters better mobility and stability for walking and running.
Ankle Sprains
Manual therapy techniques can help realign the ankle joint, reduce swelling, and normalize soft tissue function. By addressing ligament tension and muscle imbalances, therapy promotes quicker healing and better balance. It also aids in preventing chronic instability and recurrent sprains.
Arthritis
Gentle mobilizations and soft tissue work can improve joint nutrition and decrease stiffness related to osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. This approach helps relieve discomfort, improves range of motion, and enhances overall function. With consistent sessions, individuals often experience better daily movement and less reliance on pain medications.
Bicipital Tendinitis
By targeting adhesions and tight fascia around the biceps tendon, manual therapy can reduce inflammation and pain. Techniques like myofascial release alleviate pressure, helping restore normal arm movement. This hands-on approach supports healthier tendon function and diminishes the risk of further irritation.
Bony Fractures
After a fracture has healed, manual therapy assists in restoring flexibility and normal movement patterns around the injured area. It addresses scar tissue, muscle tightness, and joint restrictions that can develop while immobilized. This careful manipulation helps you regain function and confidence sooner.
Bursitis (hip, pes anserine, or shoulder)
Through targeted pressure and joint mobilizations, manual therapy reduces inflammation and muscular tension around irritated bursae. This hands-on care promotes better movement and eases pain during daily activities. Over time, patients often find increased comfort and fewer painful flare-ups.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Manual therapy helps release tension and pressure within the wrist and forearm, reducing median nerve compression. Skilled mobilizations encourage smoother tendon gliding, relieving pain and numbness in the hand. Regular treatment can restore grip strength and help you return to daily tasks with less discomfort.
Concussion
Post-concussion symptoms like neck stiffness and headaches may be relieved with gentle manual therapy. Hands-on techniques relax tight muscles and improve blood flow, supporting a calmer, more balanced state. By easing tension, therapy also enhances comfort and can speed the overall recovery process.
De Quervain’s Syndrome
Manual therapy focuses on relieving tension in the thumb tendons and surrounding tissues, decreasing inflammation. Soft tissue techniques and joint glides help restore normal movement and reduce pain. Over time, improved tendon mobility can lessen stress in daily thumb or wrist motions.
Degenerative Disc Disease
Gentle mobilizations and soft tissue work reduce excessive pressure on discs and adjacent structures, helping alleviate chronic back or neck pain. By restoring better spinal mechanics, manual therapy supports healthier disc function. This hands-on approach can help slow further degeneration and maintain comfort in daily movement.
Disc Displacement
Hands-on techniques can help relieve muscular guarding and promote proper spinal alignment, allowing the displaced disc to recede from nerve structures. Careful mobilization aims to reduce pain and enhance range of motion. This therapy supports more efficient healing and helps avoid recurring back or neck flare-ups.
Elbow Epicondylitis (lateral or medial)
Commonly known as tennis or golfer’s elbow, this condition responds well to manual therapy, which reduces tension in forearm muscles and tendons. Trigger point work and joint glides diminish inflammation, helping to restore pain-free elbow movement. It’s a valuable component of a comprehensive rehab plan.
Frozen Shoulder
Manual therapy eases tightness in the shoulder capsule and surrounding muscles, helping to restore range of motion. Myofascial release and joint mobilizations reduce pain and stiffness, improving daily function. Used alongside stretching exercises, these hands-on techniques can significantly accelerate recovery.
Headaches (cervicogenic, migraine, tension)
Tight neck and upper back muscles often trigger or worsen headaches. Manual therapy techniques relax these areas, improving spinal alignment and circulation. With less tension and pressure, headache frequency and intensity can be reduced, enhancing overall well-being.
Impingement Syndrome
By mobilizing the shoulder joint and loosening surrounding soft tissues, manual therapy reduces the painful friction associated with impingement. Restored mechanics help the rotator cuff move smoothly beneath the acromion. Regular sessions can improve shoulder comfort and function.
IT Band Syndrome
Manual therapy relieves tension along the iliotibial band, reducing friction at the knee or hip. Combining myofascial release with gentle stretching fosters healthy tissue movement and eases pain. For runners or athletes, this hands-on approach can be key to preventing recurrences.
Jaw Pain or Temporomandibular Disorder (TMJ)
Gentle manipulations of the jaw and soft tissues around the face and neck can reduce tension and improve TMJ function. This eases pain, reduces clicking or locking, and fosters better jaw mobility. Patients often find it relieves associated headaches and neck strain as well.
Joint Replacement (hip, knee, shoulder)
Manual therapy supports prosthetic joint function by reducing tension in nearby muscles and ligaments. Mobilizing tissues ensures smoother movements and helps you adapt to the new joint more quickly. Gentle manipulation can also minimize scar tissue and ease discomfort during rehabilitation.
Joint Sprains (ankle, back, knee, neck, shoulder)
Whether minor or severe, sprains often benefit from manual therapy to reduce swelling, restore joint alignment, and improve tissue extensibility. Skilled mobilization helps you regain stability and function in the affected joint. Early intervention can help guard against chronic pain and re-injury.
Labral Tears (hip or shoulder)
After labral repairs or in mild tears, manual therapy helps stabilize the joint by releasing muscle tension and promoting healthy range of motion. Careful mobilizations ensure proper joint mechanics and reduce strain on the labrum. It’s an essential component to maintaining shoulder or hip function post-injury.
Low Back Pain
Chronic or acute low back pain often arises from muscle imbalances or restricted spinal segments. Manual therapy reestablishes proper lumbar alignment and loosens tight tissues, easing discomfort. This personalized approach can also minimize recurring bouts of pain.
Meniscus Tears
Manual therapy supports recovery by improving knee joint mechanics, reducing swelling, and relieving tension in supporting muscles. Targeted manipulations can help protect the healing meniscus and promote smoother motion. As part of a broader rehabilitation plan, it often accelerates a safer return to activity.
Muscle Spasms
Tight, knotted muscles can be “reset” through hands-on treatment that reduces spasm and restores healthy circulation. Releasing tension in overactive tissues helps break the pain-spasm cycle, allowing you to move more freely. Consistent therapy may also prevent future muscular flare-ups.
Muscle Strains (Biceps, Calf, Hamstring, Pec, Quadriceps, Rotator Cuff)
Hands-on care decreases scar tissue formation and boosts blood flow to accelerate healing of strained muscles. Techniques like soft tissue mobilization and gentle stretching reduce pain and restore elasticity. Integrating manual therapy with exercise can lead to quicker, more complete recoveries.
Neck Pain
Manual techniques targeting stiff segments and tight neck muscles help restore pain-free rotation and flexion. By improving alignment and circulation, therapy eases nerve irritation and tension headaches. This comprehensive approach often yields long-term relief and healthier posture.
Piriformis Syndrome
By releasing tension in the piriformis and surrounding tissues, manual therapy eases sciatic nerve compression. This improves hip mobility, diminishes radiating pain, and facilitates more comfortable movement. Consistent treatment can provide sustained relief for those with persistent symptoms.
Plantar Fasciitis
Manual therapy on the foot and calf muscles releases tension in the plantar fascia, reducing pain and inflammation. By restoring elasticity and improving circulation, it helps the body heal from repetitive stress. This approach can speed recovery and lower the chance of chronic heel pain.
Postural Dysfunction
Manual therapy helps correct misalignments and muscle imbalances caused by prolonged sitting or poor posture. Gentle adjustments improve spinal curvature and ease strain on surrounding tissues. Coupled with strengthening and ergonomic guidance, it supports a healthier, upright stance.
Radiculopathy (Cervical and Lumbar)
When nerve roots are compressed, manual therapy can alleviate the muscular and joint tightness contributing to the pressure. Carefully applied techniques free up nerve pathways, often reducing pain, numbness, or tingling. This approach helps restore comfortable, normal movement in the arms or legs.
Rotator Cuff Tear
Manual therapy aims to relieve joint restrictions and muscle tension around the shoulder, enhancing blood flow to support tissue healing. Carefully mobilizing the scapula and shoulder complex reduces pain and promotes better overhead movement. This approach is especially useful alongside post-surgical rehab exercises.
Sacroiliac Dysfunction
With specific mobilizations and soft tissue release around the pelvis, manual therapy can stabilize the sacroiliac joint. This lessens low back and hip pain by improving load distribution across the hips and spine. A consistent treatment plan fosters more reliable movement and alignment.
Sciatica
Manual techniques help reduce lower back, gluteal, and hamstring tension that may press on the sciatic nerve. Alleviating these restrictions can lessen pain radiating down the leg. Over time, improved nerve mobility and muscle balance support a healthier, pain-free gait.
Scoliosis
Manual therapy can ease muscle imbalances that exacerbate spinal curvature. Targeted mobilizations help improve symmetry, reduce discomfort, and promote healthier posture. When combined with bracing or exercises, it can enhance overall quality of life for those with scoliosis.
Shin Splints
Releasing tension and improving alignment in the lower leg can ease the repetitive stress that causes shin splints. Manual therapy helps correct biomechanical faults in the foot and ankle, reducing strain on the shin. This approach is particularly helpful for active individuals seeking quick relief.
Spinal Stenosis
Targeted manual therapy can open up restricted areas of the spine, alleviating pressure on nerves in patients with stenosis. Gentle mobilizations and soft tissue work encourage more space within the spinal canal, helping reduce pain and improve walking tolerance. Regular treatment supports functional independence.
Whiplash
After a neck injury from car accidents or sudden impacts, manual therapy soothes overstretched ligaments and tight cervical muscles. Techniques that carefully mobilize the neck and upper back reduce pain and restore normal spinal curves. This approach is essential for regaining comfort and preventing chronic neck issues.
Common Questions About Certified Manual Therapy
1. Does manual therapy hurt?
While you may experience mild discomfort or pressure during certain techniques, Certified Manual Therapists are trained to work within your comfort level. They’ll adjust intensity based on your feedback, aiming to relieve tension, not create more pain. Often, people feel immediate relief or improved range of motion after a session.
2. How is Certified Manual Therapy different from regular massage?
Massage primarily focuses on relaxing muscles and can be part of manual therapy, but Certified Manual Therapy is more comprehensive. It may include joint mobilizations, nerve glides, and advanced soft tissue techniques to address specific dysfunctions. Therapists also assess posture, movement patterns, and range of motion to tailor a targeted treatment plan.
3. Who benefits the most from manual therapy?
Individuals dealing with pain, stiffness, or limited joint mobility often see significant improvements. Whether recovering from surgery, managing chronic conditions like arthritis, or healing from a sports injury, manual therapy can help. It’s especially effective for people who need a personalized, hands-on approach to resolving underlying issues.
4. How many sessions do I need?
Treatment frequency varies based on your condition and goals. Some experience noticeable relief within a few sessions, while others require a longer plan to address complex or long-standing issues. Your therapist will assess your progress each visit and adapt the plan, ensuring you receive the most effective care.
5. Can manual therapy help prevent future injuries?
Absolutely. By improving joint mechanics, muscle balance, and posture, manual therapy addresses the root causes of recurring pain or injuries. Therapists also provide advice on exercises and ergonomics, helping you maintain better alignment and reduce the likelihood of re-injury. Regular “tune-up” sessions can support lasting health benefits.
6. Is there any downtime after a session?
You might feel some mild soreness or fatigue, similar to after a workout, but most people can resume normal activities immediately. In fact, many experience increased mobility right away. Your therapist may recommend light stretching, hydration, or gentle movement afterward to maximize your results and alleviate any lingering soreness.
7. Can manual therapy be combined with other treatments?
Yes. Manual therapy often complements exercises, modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation, and lifestyle recommendations. A multifaceted approach addresses your condition from multiple angles, potentially speeding your recovery. Your therapist will create a balanced plan that adapts as you progress, ensuring all aspects of your care work together effectively.